Gram positive bacteria crossword clue – Embarking on a scientific expedition, we delve into the fascinating realm of Gram-positive bacteria, exploring their unique characteristics, identification techniques, and clinical implications. The Gram-positive bacteria crossword clue serves as our guiding light, illuminating the path towards a comprehensive understanding of these microorganisms.
Their distinct cell wall structure, intricate Gram-staining procedure, and diverse clinical manifestations paint a captivating picture of these bacterial inhabitants. Join us as we unravel the secrets of Gram-positive bacteria, their impact on human health, and the strategies employed to combat their infections.
Characteristics of Gram-Positive Bacteria: Gram Positive Bacteria Crossword Clue
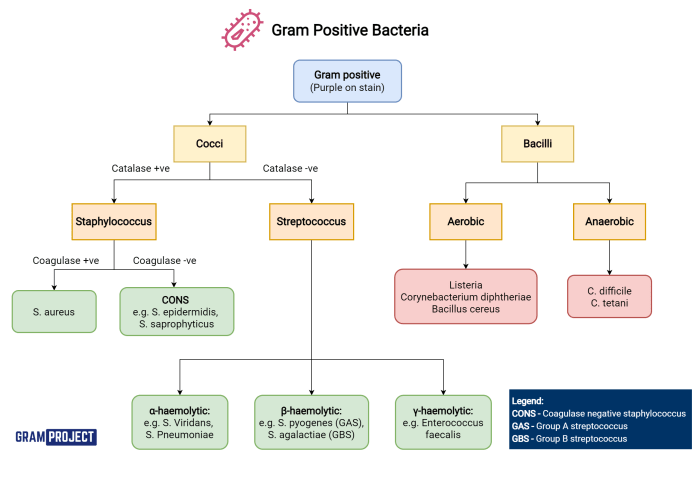
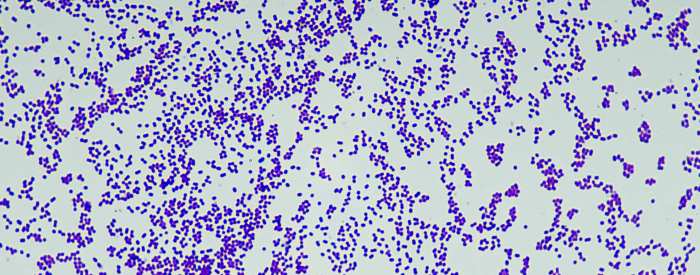
Gram-positive bacteria are a group of bacteria that are characterized by their ability to retain the Gram stain, a purple dye used to differentiate between different types of bacteria. This ability is due to the structure of their cell wall.
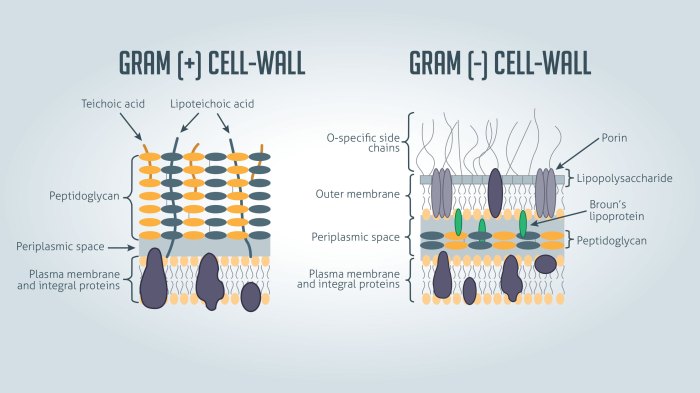
The cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria is composed of a thick layer of peptidoglycan, a polymer made up of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid. The peptidoglycan layer is cross-linked by short peptides, which gives the cell wall its strength and rigidity.
The thick cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria makes them more resistant to antibiotics than Gram-negative bacteria. This is because the antibiotics cannot easily penetrate the cell wall and reach the target site within the bacteria.
Gram-Staining Procedure, Gram positive bacteria crossword clue
The Gram-staining procedure is a laboratory technique used to differentiate between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The procedure involves the following steps:
- A smear of bacteria is made on a microscope slide and heat-fixed.
- The slide is flooded with crystal violet, a purple dye, and allowed to sit for 1 minute.
- The slide is rinsed with water.
- The slide is flooded with Gram’s iodine, a mordant, and allowed to sit for 1 minute.
- The slide is rinsed with water.
- The slide is decolorized with alcohol for 10-15 seconds.
- The slide is rinsed with water.
- The slide is counterstained with safranin, a red dye, and allowed to sit for 1 minute.
- The slide is rinsed with water and allowed to air dry.
Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet-iodine complex and appear purple under the microscope. Gram-negative bacteria do not retain the crystal violet-iodine complex and appear red under the microscope.
| Gram-Positive Bacteria | Gram-Negative Bacteria |
|---|---|
| Retain crystal violet-iodine complex | Do not retain crystal violet-iodine complex |
| Appear purple under the microscope | Appear red under the microscope |
Identification of Gram-Positive Bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria can be identified using a variety of methods, including:
- Selective media:Selective media are used to isolate Gram-positive bacteria from other types of bacteria. Selective media contain antibiotics that are effective against Gram-negative bacteria but not against Gram-positive bacteria.
- Biochemical tests:Biochemical tests can be used to identify Gram-positive bacteria based on their ability to metabolize different substrates. For example, the catalase test can be used to identify Gram-positive bacteria that produce the enzyme catalase.
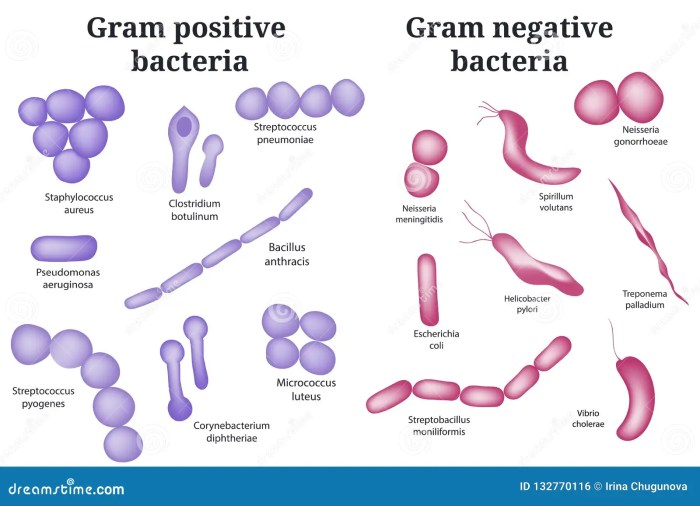
Some common Gram-positive bacteria include:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Bacillus subtilis
Gram-positive bacteria are responsible for a wide range of infections, including skin and soft tissue infections, pneumonia, and meningitis.
Antibiotic Susceptibility of Gram-Positive Bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria are susceptible to a variety of antibiotics, including:
- Penicillins:Penicillins are a class of antibiotics that inhibit the synthesis of peptidoglycan, the major component of the bacterial cell wall. Penicillins are effective against Gram-positive bacteria but not against Gram-negative bacteria.
- Cephalosporins:Cephalosporins are a class of antibiotics that are similar to penicillins but have a broader spectrum of activity. Cephalosporins are effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
- Vancomycin:Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic that is used to treat infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics.
| Antibiotic | Mechanism of Action | Spectrum of Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Penicillins | Inhibit synthesis of peptidoglycan | Gram-positive bacteria |
| Cephalosporins | Inhibit synthesis of peptidoglycan | Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria |
| Vancomycin | Inhibit synthesis of peptidoglycan | Gram-positive bacteria |
Clinical Significance of Gram-Positive Bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria are responsible for a wide range of infections, including:
- Skin and soft tissue infections:Gram-positive bacteria are the most common cause of skin and soft tissue infections, such as cellulitis and abscesses.
- Pneumonia:Gram-positive bacteria are a common cause of pneumonia, an infection of the lungs.
- Meningitis:Gram-positive bacteria are a common cause of meningitis, an infection of the membranes that line the brain and spinal cord.
Gram-positive bacteria can also cause more serious infections, such as:
- Sepsis:Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that occurs when bacteria enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body.
- Endocarditis:Endocarditis is an infection of the lining of the heart.
- Osteomyelitis:Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone.
Gram-positive bacteria are becoming increasingly resistant to antibiotics, which makes it more difficult to treat infections caused by these bacteria.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the defining characteristic of Gram-positive bacteria?
Gram-positive bacteria possess a thick cell wall composed primarily of peptidoglycan.
How does the Gram-staining procedure differentiate Gram-positive from Gram-negative bacteria?
Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet-iodine complex during the Gram-staining process, resulting in a purple color, while Gram-negative bacteria do not.
Name a common Gram-positive bacterium and its clinical significance.
Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive bacterium known for causing a wide range of infections, including skin and soft tissue infections, pneumonia, and sepsis.