The equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue, a versatile pH indicator, holds immense significance in understanding its behavior and practical applications. This article delves into the concept of the equilibrium constant, explores factors that influence it, and discusses its crucial role in various fields.
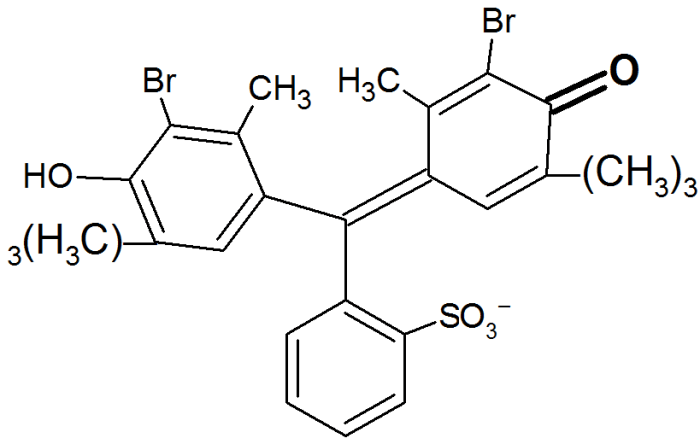
The equilibrium constant provides a quantitative measure of the extent to which a chemical reaction proceeds towards completion. In the case of bromothymol blue, the equilibrium constant governs the interconversion between its acid and base forms, influencing its color change over a specific pH range.
Equilibrium Constant for Bromothymol Blue
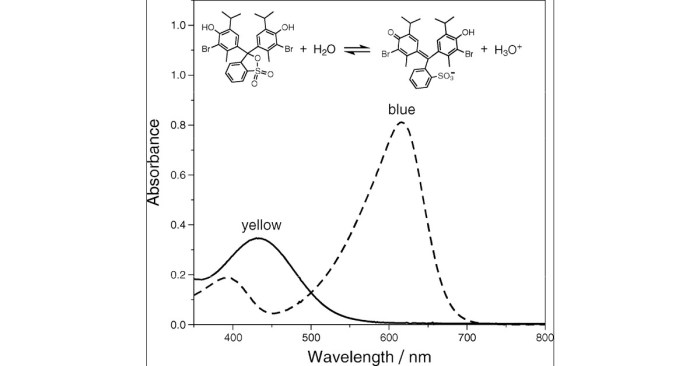
Bromothymol blue is a weak acid that undergoes a color change from yellow to blue as the pH of a solution changes. The equilibrium constant for this color change can be used to determine the pH of a solution.
Equilibrium Constant Expression
The equilibrium constant expression for bromothymol blue is:
“`K = [H+][In-] / [HIn]“`
where:
- [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ions
- [In-] is the concentration of the blue form of bromothymol blue
- [HIn] is the concentration of the yellow form of bromothymol blue
Significance of the Equilibrium Constant
The equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue is a measure of the strength of the acid. A larger equilibrium constant indicates that the acid is stronger and will dissociate more completely in water. The equilibrium constant can also be used to calculate the pH of a solution at a given concentration of bromothymol blue.
Factors Affecting the Equilibrium Constant, Equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue
The equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue is affected by several factors, including:
Temperature
The equilibrium constant increases with increasing temperature. This is because the dissociation of bromothymol blue is an endothermic process, and increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right.
pH
The equilibrium constant decreases with increasing pH. This is because the dissociation of bromothymol blue is suppressed at higher pH values.
Ionic Strength
The equilibrium constant decreases with increasing ionic strength. This is because the presence of other ions in solution reduces the activity of the hydrogen ions.
Applications of the Equilibrium Constant
The equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue has a number of practical applications, including:
Acid-Base Titrations
The equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue can be used to determine the endpoint of an acid-base titration. The endpoint is the point at which the moles of acid added are equal to the moles of base present. At the endpoint, the pH of the solution will be equal to the pKa of bromothymol blue.
Other Applications
The equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue can also be used in a variety of other applications, such as:
- Determining the pH of natural waters
- Studying the kinetics of acid-base reactions
- Developing new pH sensors
Experimental Determination of the Equilibrium Constant
The equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue can be determined experimentally using a variety of methods, including:
Spectrophotometry
Spectrophotometry is a method that measures the absorbance of light by a solution. The absorbance of a solution is proportional to the concentration of the colored species in the solution. The equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue can be determined by measuring the absorbance of a solution of bromothymol blue at different pH values.
Potentiometry
Potentiometry is a method that measures the electrical potential of a solution. The electrical potential of a solution is proportional to the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution. The equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue can be determined by measuring the electrical potential of a solution of bromothymol blue at different pH values.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
The data from an equilibrium constant determination can be analyzed using a variety of methods, including:
Linear Regression
Linear regression is a method that can be used to determine the slope and intercept of a linear relationship. The slope of the linear relationship between the absorbance of a solution of bromothymol blue and the pH of the solution is equal to the equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue.
Nonlinear Regression
Nonlinear regression is a method that can be used to determine the parameters of a nonlinear relationship. The parameters of the nonlinear relationship between the electrical potential of a solution of bromothymol blue and the pH of the solution can be used to determine the equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue.
FAQ Explained: Equilibrium Constant For Bromothymol Blue
What is the equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue?
The equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue is a numerical value that represents the ratio of the concentrations of its acid and base forms at equilibrium.
How does temperature affect the equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue?
Temperature can influence the equilibrium constant by altering the relative stability of the acid and base forms of bromothymol blue.
What is the practical significance of the equilibrium constant for bromothymol blue?
The equilibrium constant is crucial for understanding the behavior of bromothymol blue as a pH indicator and its applications in acid-base titrations.