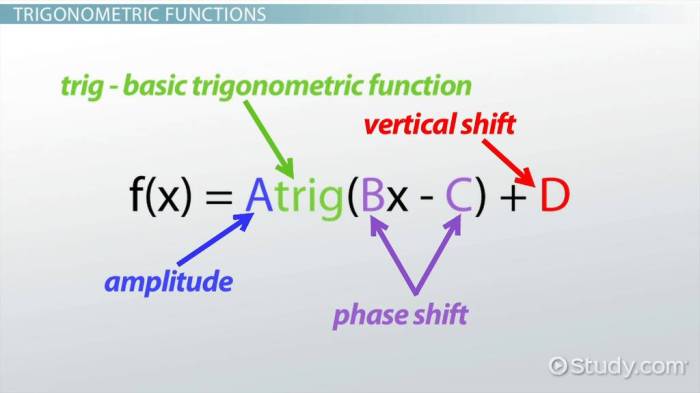
Graphing skill #1 what type of graph is it – In the realm of data visualization, graphing skills reign supreme, empowering us to transform raw numbers into compelling visual representations. Among the myriad of graphing techniques, one stands out as the foundation: identifying the appropriate graph type for the data at hand.
Embark on this journey as we delve into the intricacies of graphing skill #1, deciphering the enigmatic world of graphs.
From the ubiquitous line graph to the insightful scatter plot, each graph type possesses unique characteristics and applications. Line graphs eloquently depict trends over time, while bar graphs provide insightful comparisons between categories. Pie charts, with their colorful slices, reveal the proportions within a whole, and scatter plots illuminate relationships between variables.
As we progress, we’ll uncover the advantages and limitations of each graph type, equipping you with the knowledge to select the most effective visual representation for your data.
1. Overview of Graphing Skills: Graphing Skill #1 What Type Of Graph Is It
Graphing skills involve the ability to represent data visually using graphs and charts. They are essential in various fields, including science, engineering, business, and education, as they allow individuals to analyze and interpret data effectively.
Different types of graphs are used for specific purposes. Line graphs are used to track changes over time, bar graphs compare different categories, pie charts show proportions, scatter plots explore relationships between variables, histograms display frequency distributions, box plots summarize data distributions, tree diagrams visualize hierarchical structures, and flowcharts illustrate processes or algorithms.
2. Types of Graphs
Line Graphs, Graphing skill #1 what type of graph is it
Line graphs connect data points with lines, making them ideal for showing trends and changes over time. They are commonly used in finance, economics, and scientific research to track variables such as stock prices, economic indicators, or experimental results.
Advantages:
- Easily show trends and patterns
- Allow for comparisons between multiple variables
Limitations:
- Can be misleading if data points are not evenly spaced
- May not be suitable for categorical data
Bar Graphs
Bar graphs use rectangular bars to compare different categories or groups of data. They are commonly used in surveys, market research, and business presentations to compare sales figures, customer demographics, or survey responses.
Advantages:
- Easy to understand and interpret
- Suitable for comparing categorical data
Limitations:
- Can be cluttered if there are too many categories
- May not be suitable for showing trends over time
Pie Charts
Pie charts are circular graphs divided into sectors, where each sector represents a proportion of the whole. They are commonly used to show the relative sizes of different categories or components. For example, a pie chart can show the market share of different companies in an industry.
Advantages:
- Easy to visualize proportions
- Suitable for showing the relative size of categories
Limitations:
- Can be misleading if there are too many categories
- May not be suitable for showing trends over time
Essential Questionnaire
What is the most versatile graph type?
Line graphs are highly versatile, suitable for displaying trends, comparisons, and distributions.
When should I use a pie chart?
Pie charts are ideal for illustrating the proportions within a whole, especially when comparing different categories.
What is the difference between a scatter plot and a line graph?
Scatter plots display the relationship between two variables, while line graphs depict trends over time or across categories.