The Pseudomonas aeruginosa nitrate reduction test is a valuable tool in the field of microbiology, providing insights into the metabolic capabilities of bacterial species. This test determines the ability of bacteria to convert nitrate into nitrite, a process that plays a crucial role in the nitrogen cycle and can aid in the identification and differentiation of bacteria.
The principle of the nitrate reduction test lies in the enzymatic conversion of nitrate to nitrite by the enzyme nitrate reductase. This reaction is indicative of the bacterium’s ability to utilize nitrate as an alternative electron acceptor under anaerobic conditions.
The test involves inoculating a bacterial culture into a nitrate-containing medium and observing the production of nitrite over time.
Introduction
The nitrate reduction test is a biochemical test used to determine the ability of bacteria to reduce nitrate to nitrite. This test is important for identifying and differentiating bacteria, as well as for understanding their metabolic pathways.
Principle of the Test

The nitrate reduction test is based on the ability of certain bacteria to use nitrate as an electron acceptor in the absence of oxygen. The enzyme nitrate reductase catalyzes the reduction of nitrate to nitrite, which can then be further reduced to ammonia or nitrogen gas.
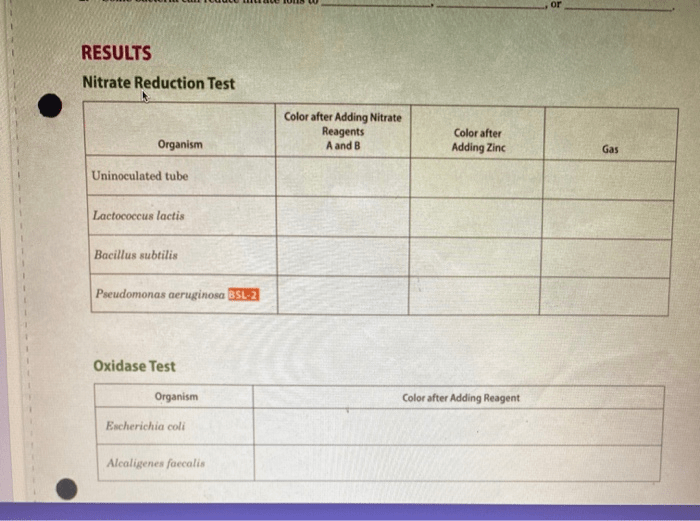
Procedure for Nitrate Reduction Test, Pseudomonas aeruginosa nitrate reduction test
- Inoculate a tube of nitrate broth with the test organism.
- Incubate the tube at 35°C for 24-48 hours.
- Add a few drops of sulfanilic acid and α-naphthylamine to the tube.
- Observe the color of the tube.
Interpretation of Results: Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Nitrate Reduction Test
A positive nitrate reduction test is indicated by the development of a red color in the tube. This indicates that the test organism is able to reduce nitrate to nitrite.
A negative nitrate reduction test is indicated by the absence of a red color in the tube. This indicates that the test organism is unable to reduce nitrate to nitrite.
Clinical Applications

The nitrate reduction test is used to identify and differentiate bacteria. It is particularly useful for identifying members of the Enterobacteriaceae family, as well as for differentiating between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other non-fermenting Gram-negative bacteria.
Troubleshooting
- If the test organism does not grow in the nitrate broth, the test may be invalid.
- If the test organism grows but does not reduce nitrate, the test may be negative due to the presence of inhibitors in the medium.
- If the test organism reduces nitrate but does not produce a red color, the sulfanilic acid or α-naphthylamine may have been added incorrectly.
Advantages and Limitations
- Advantages:
- Simple and inexpensive to perform.
- Can be used to identify and differentiate bacteria.
- Can be used to study the metabolic pathways of bacteria.
- Limitations:
- Not all bacteria can reduce nitrate.
- The test can be affected by the presence of inhibitors in the medium.
- The test does not provide information about the specific products of nitrate reduction.
- Nitrate reductase assay
- Nitrite reductase assay
- Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
Alternatives to Nitrate Reduction Test
There are a number of alternative methods for detecting nitrate reduction in bacteria. These methods include:
These methods are more sensitive and specific than the nitrate reduction test, but they are also more expensive and time-consuming to perform.
Question Bank
What is the purpose of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa nitrate reduction test?
The nitrate reduction test determines the ability of bacteria to convert nitrate into nitrite, providing insights into their metabolic capabilities and aiding in bacterial identification.
How is the nitrate reduction test performed?
The test involves inoculating a bacterial culture into a nitrate-containing medium and observing the production of nitrite over time, indicating the presence of nitrate reductase enzyme.
What is the significance of a positive nitrate reduction test result?
A positive result indicates the bacterium’s ability to utilize nitrate as an alternative electron acceptor under anaerobic conditions, providing an additional source of energy for the bacterium.
What are the limitations of the nitrate reduction test?
The test may not be sensitive enough to detect all nitrate-reducing bacteria, and some bacteria may produce nitrite through alternative pathways, leading to false-positive results.