Chapter 1 the human body an orientation answer key – Chapter 1: The Human Body An Orientation Answer Key presents a comprehensive overview of the human body, its organization, and its essential components. This chapter lays the foundation for understanding the structure and function of the human body, providing a solid base for further exploration in anatomy and physiology.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
1. The Human Body
An Introduction
The human body is a highly complex system composed of organs and tissues that work together to maintain life. Each organ system serves a specific function, contributing to the overall health and well-being of the organism.
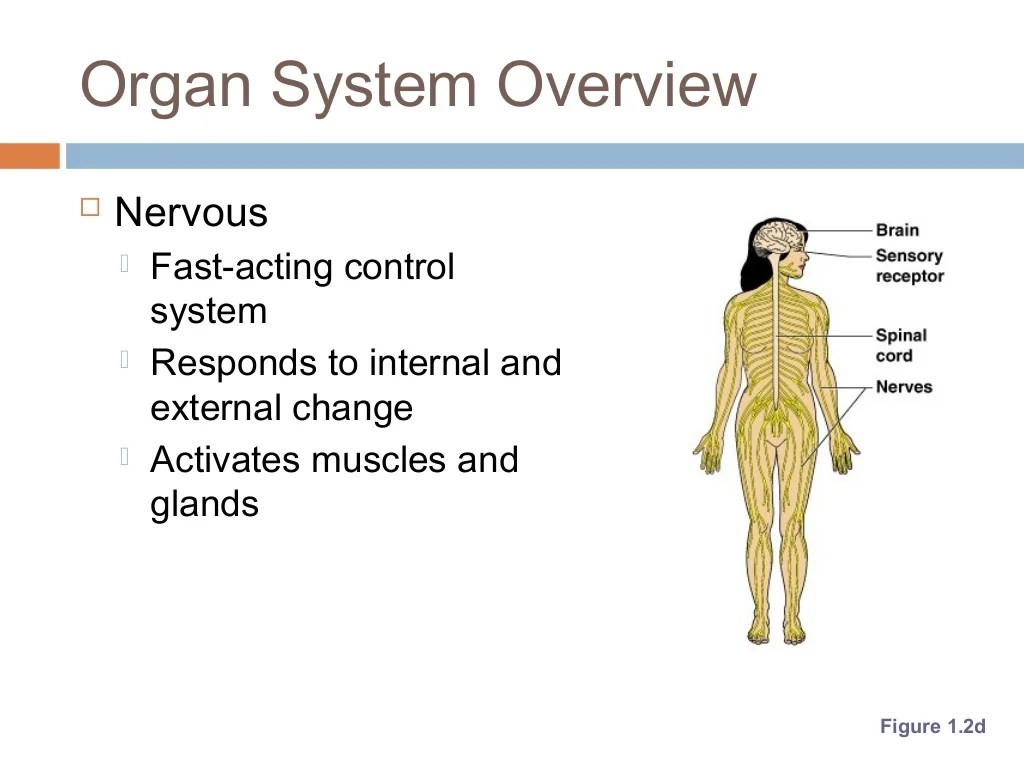
Major organ systems include the circulatory system, responsible for transporting blood and oxygen; the respiratory system, involved in gas exchange; the digestive system, responsible for nutrient absorption; the urinary system, responsible for waste elimination; and the nervous system, responsible for communication and control.
2. Body Organization
The human body is organized hierarchically, from the smallest units (cells) to larger structures (tissues, organs, and organ systems). Cells are the fundamental units of life, forming tissues, which are groups of similar cells that perform specific functions. Organs are composed of multiple tissues and perform specific tasks within an organ system.
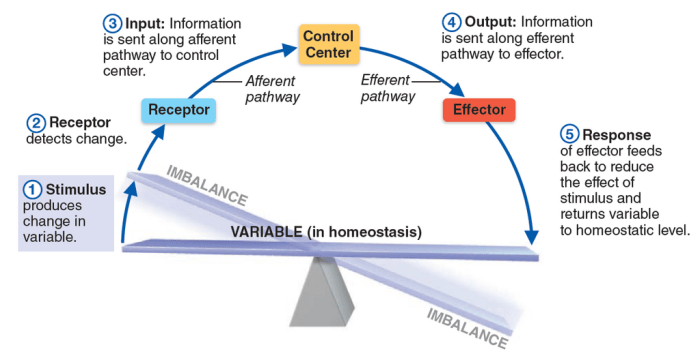
Homeostasis is the body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. This is essential for optimal functioning of the body’s cells and organs.
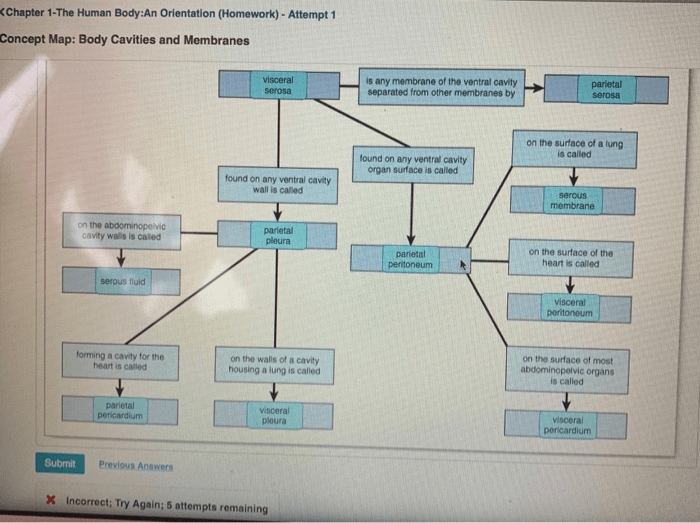
3. Body Cavities and Membranes
The human body contains several body cavities, each lined with serous membranes. These cavities provide protection and support for the organs they contain.
- Cranial cavity: Houses the brain.
- Spinal cavity: Houses the spinal cord.
- Thoracic cavity: Houses the heart, lungs, and other structures.
- Abdominal cavity: Houses the digestive organs, kidneys, and other structures.
- Pelvic cavity: Houses the reproductive organs and urinary bladder.
Serous membranes consist of two layers: the parietal layer, which lines the body cavity, and the visceral layer, which covers the organs. They secrete a fluid that reduces friction between the organs and the cavity walls.
4. Body Planes and Sections
Anatomical planes are imaginary lines used to divide the body into sections for study and reference. The three main planes are:
- Sagittal plane: Divides the body into left and right halves.
- Frontal plane: Divides the body into anterior and posterior halves.
- Transverse plane: Divides the body into superior and inferior halves.
Cross-sectional views are created by cutting the body along these planes, providing insights into the internal anatomy.
5. Body Regions and Directional Terms
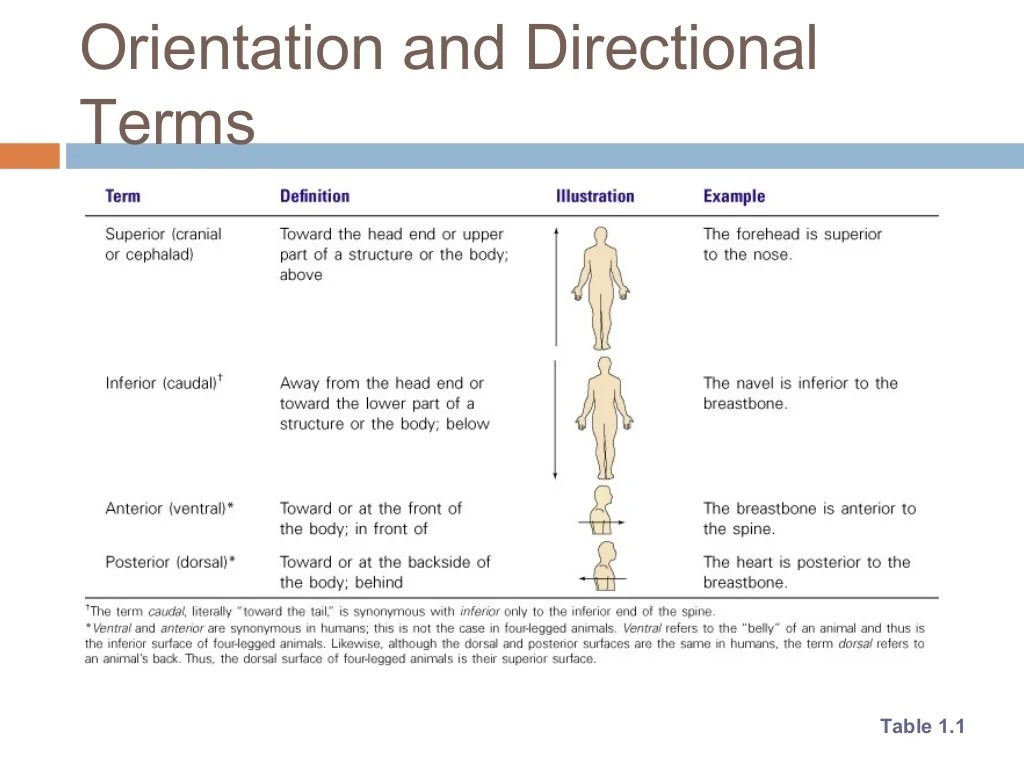
The human body is divided into anatomical regions for descriptive purposes. These regions include the head, neck, trunk, upper limbs, and lower limbs.
Directional terms are used to describe the relative positions of body structures. Common directional terms include:
- Anterior: Front
- Posterior: Back
- Superior: Above
- Inferior: Below
- Medial: Toward the midline
- Lateral: Away from the midline
- Proximal: Closer to the point of attachment
- Distal: Farther from the point of attachment
User Queries: Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation Answer Key
What is the hierarchical organization of the human body?
The human body is organized hierarchically from cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems.
What is homeostasis?
Homeostasis is the ability of the body to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in the external environment.
What are the major body cavities?
The major body cavities are the cranial cavity, thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, and pelvic cavity.
What are the anatomical planes used to describe the human body?
The anatomical planes used to describe the human body are the sagittal plane, frontal plane, and transverse plane.
What are the anatomical regions of the body?
The anatomical regions of the body include the head, neck, trunk, upper limbs, and lower limbs.