Which type of bacterial reproduction is depicted in the diagram – The realm of bacterial reproduction, a subject of paramount importance, unfolds before us as we embark on a journey to decipher the intricate mechanisms that govern the propagation of these microscopic organisms. Through the lens of a meticulously crafted diagram, we shall endeavor to identify the specific mode of bacterial reproduction it portrays, unraveling its defining characteristics and exploring its implications for the bacterial world and beyond.
The diagram under scrutiny serves as a visual representation of a particular bacterial reproduction method, capturing its essence through the depiction of key structures and processes. By dissecting the diagram’s components and tracing the depicted sequence of events, we can deduce the underlying reproductive strategy employed by the bacteria in question.
Bacterial Reproduction Methods
Bacteria employ diverse reproduction methods to ensure their survival and adaptation in various environments. These methods include binary fission, conjugation, transformation, and transduction.
Binary Fission, Which type of bacterial reproduction is depicted in the diagram
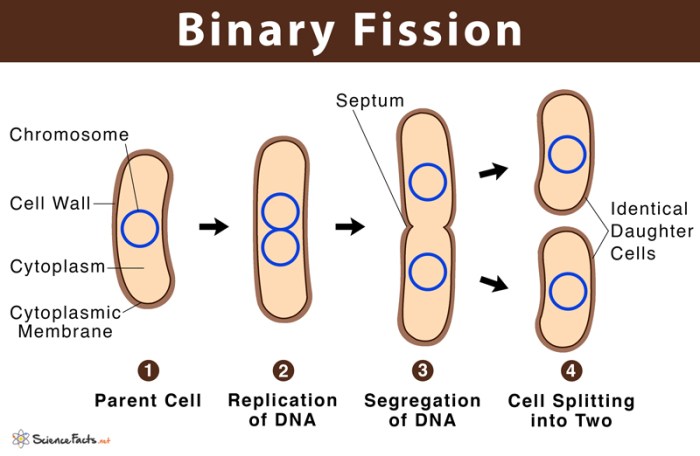
Binary fission is the most common form of bacterial reproduction. It involves the division of a single parent cell into two genetically identical daughter cells. The process begins with DNA replication, followed by the formation of a septum, which divides the cell into two halves.
Each daughter cell inherits one copy of the replicated DNA.
Conjugation
Conjugation is a process of genetic exchange between two bacteria cells that are in physical contact. A pilus, a hair-like structure, extends from the donor cell and connects to the recipient cell. Through the pilus, a copy of the donor cell’s plasmid, a small circular DNA molecule, is transferred to the recipient cell.
Transformation
Transformation is the process by which bacteria take up free DNA from the environment and incorporate it into their own genome. The DNA may come from a dead bacteria cell or from a virus that has infected the cell. Transformation is a rare event but can provide bacteria with new genes that confer beneficial traits.
Transduction
Transduction is the process by which bacteria transfer DNA from one cell to another through a virus. The virus infects the donor cell and incorporates some of the cell’s DNA into its own genome. When the virus infects the recipient cell, it injects the donor cell’s DNA into the cell, which can then be incorporated into the recipient cell’s genome.
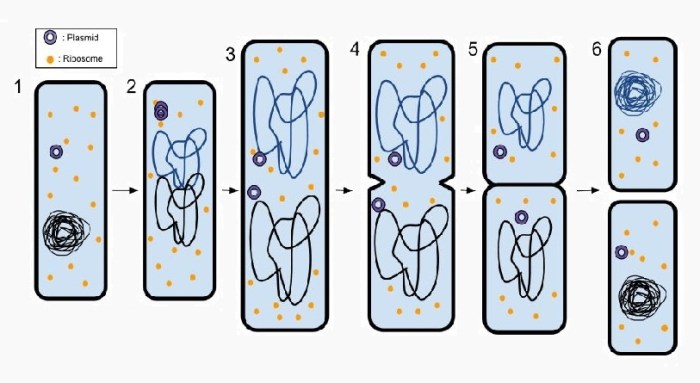
Diagram Analysis
The provided diagram depicts binary fission, the most common form of bacterial reproduction. The diagram shows a single parent cell that is dividing into two daughter cells. The following key characteristics of binary fission are illustrated in the diagram:
- The parent cell is shown with a single, circular chromosome.
- The chromosome is replicating, with two copies of the chromosome visible.
- A septum is forming, dividing the cell into two halves.
- Each daughter cell will inherit one copy of the replicated chromosome.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Reproduction Methods
| Reproduction Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Binary Fission | – Fast and efficient
|
– Can lead to genetic homogeneity
|
| Conjugation | – Allows for genetic exchange
|
– Requires physical contact between cells
|
| Transformation | – Can provide bacteria with new genes from the environment
|
– Rare event
|
| Transduction | – Can transfer DNA between bacteria that are not in physical contact
|
– Requires the presence of a virus
|
Ecological Implications of Bacterial Reproduction
The different methods of bacterial reproduction have significant implications for bacterial populations and their interactions with the environment. Binary fission allows bacteria to rapidly increase their population size, which can be beneficial in colonizing new environments or exploiting new resources.
Conjugation, transformation, and transduction can provide bacteria with new genes that confer beneficial traits, such as antibiotic resistance or the ability to metabolize new compounds. This can allow bacteria to adapt to changing environmental conditions and outcompete other organisms.
For example, the ability of bacteria to undergo conjugation has been shown to play a role in the spread of antibiotic resistance genes among bacteria populations. The transfer of antibiotic resistance genes through conjugation can lead to the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria, which are difficult to treat with antibiotics.
Similarly, transformation has been shown to play a role in the adaptation of bacteria to new environments. For example, some bacteria have acquired genes that allow them to metabolize pollutants, which can give them a competitive advantage in contaminated environments.
Answers to Common Questions: Which Type Of Bacterial Reproduction Is Depicted In The Diagram
What are the different types of bacterial reproduction?
Bacterial reproduction methods include binary fission, budding, fragmentation, and spore formation.
How does binary fission differ from budding?
Binary fission involves the division of a single bacterial cell into two identical daughter cells, while budding results in the formation of a new cell that grows out of the parent cell.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of spore formation?
Spore formation allows bacteria to survive harsh conditions, but it is a slow and energy-intensive process.