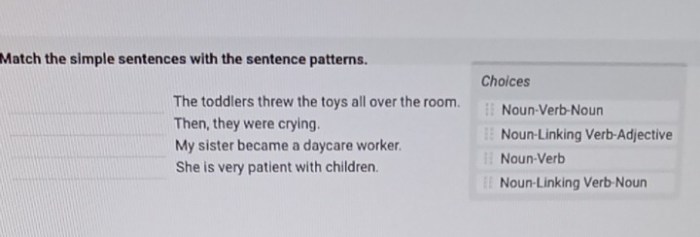
The toddlers threw the toys all over the room. – Toddlers throwing toys all over the room is a common behavior that can be frustrating for parents. However, it is important to understand that this behavior is often a normal part of toddler development. In this article, we will explore the cognitive, physical, emotional, and social factors that contribute to toy-throwing behavior in toddlers, as well as provide strategies for addressing this behavior.
Toddlers are naturally curious and eager to explore their surroundings. They are also learning how to interact with others and how to express their emotions. As a result, they may throw toys as a way to explore their environment, to get attention, or to express frustration.
Toddler Development and Behavior: The Toddlers Threw The Toys All Over The Room.

Toddlers’ cognitive and physical development can contribute to toy-throwing behavior. Their developing cognitive abilities allow them to understand the cause-and-effect relationships involved in throwing objects. They may also enjoy the sensory stimulation and physical exertion associated with throwing toys.
Emotional and social factors can also influence a toddler’s decision to throw toys. Toddlers may throw toys to express frustration, anger, or boredom. They may also throw toys to get attention or to interact with others.
Environmental Factors
The physical environment can affect toy-throwing behavior. A small or cluttered room may make it more difficult for toddlers to play safely with toys, leading to frustration and toy-throwing. Social interactions and parental behavior can also impact a toddler’s tendency to throw toys.
Toddlers may be more likely to throw toys if they are playing with other children who are also throwing toys. They may also throw toys if they are not getting enough attention from their parents.
Developmental Milestones and Toy-Throwing
Toy-throwing behavior often coincides with certain developmental milestones, such as walking and reaching. As toddlers gain these new abilities, they may explore their environment by throwing objects. They may also throw toys to practice their coordination and fine motor skills.
Strategies for Addressing Toy-Throwing, The toddlers threw the toys all over the room.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Set clear boundaries | Let toddlers know that toy-throwing is not acceptable behavior. Explain that toys are for playing, not for throwing. |
| Provide alternative outlets for energy | Give toddlers other ways to release their energy, such as running, jumping, or playing with playdough. |
| Create a structured environment | Make sure that toddlers have a safe and structured environment to play in. This will help to reduce the likelihood of toy-throwing behavior. |
Safety Considerations
Toy-throwing behavior can be a safety hazard. Toddlers may throw toys at other children or adults, causing injury. They may also throw toys at objects, such as windows or furniture, causing damage.
It is important to supervise toddlers while they are playing with toys. This will help to prevent injuries and damage to property.
- Keep toys out of reach of toddlers when they are not playing with them.
- Teach toddlers to put toys away when they are finished playing with them.
- Provide toddlers with safe toys that are appropriate for their age and development.
Clarifying Questions
Why do toddlers throw toys?
Toddlers throw toys for a variety of reasons, including exploring their environment, getting attention, or expressing frustration.
What are some strategies for addressing toy-throwing behavior?
Some strategies for addressing toy-throwing behavior include setting clear boundaries, providing alternative outlets for toddlers’ energy, and creating a structured environment that discourages toy-throwing.
Is toy-throwing behavior a sign of a problem?
Toy-throwing behavior is not typically a sign of a problem. However, if toy-throwing behavior is accompanied by other concerning behaviors, such as aggression or self-injury, it may be a sign of an underlying problem that requires professional evaluation.